RECEDING HAIRLINES IN WOMEN: CAUSES AND TREATMENTS
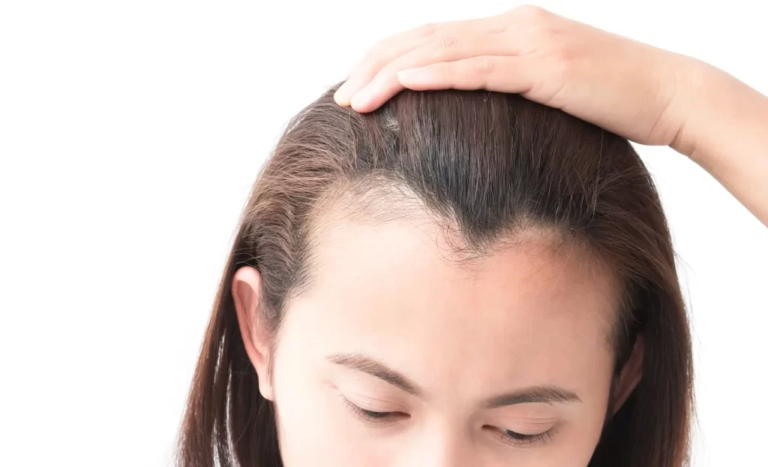
One type of hair loss that can be particularly worrisome is a receding hairlines in women, as this condition is usually more associated with men. However, women can also experience this form of hair loss, which may be distressing and impact self-confidence. Therefore, understanding the causes and available treatments is crucial in addressing this issue effectively.
What is a Receding Hairline?
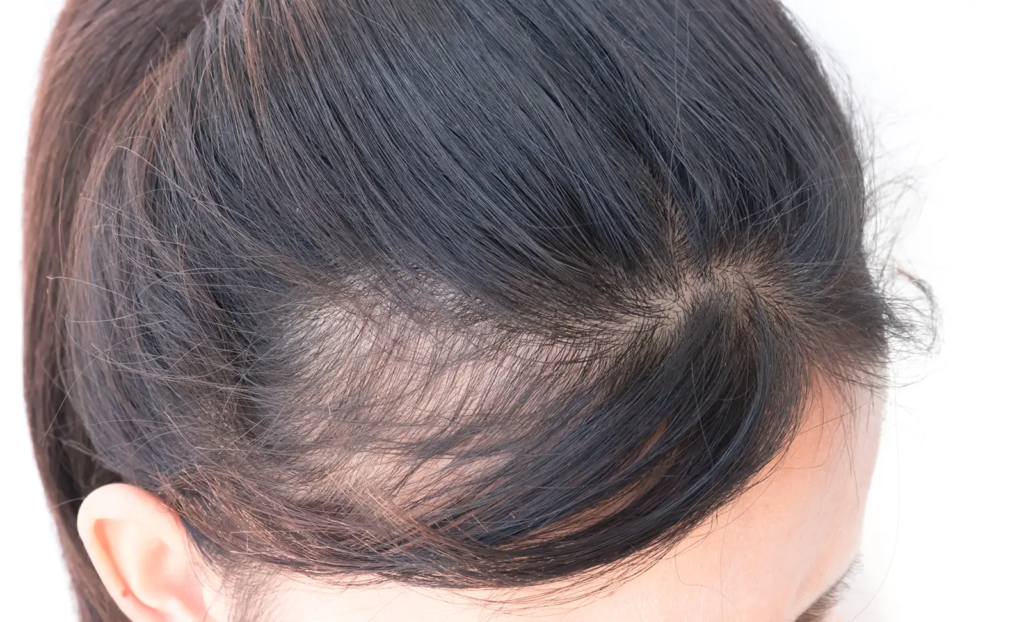
A receding hairline refers to hair loss that occurs around the frontal area of the scalp, including the temples. Over time, it pushes the hairline further back, often giving the appearance of a larger forehead or an M-shaped hairline. In some cases, the process starts gradually, making it difficult to notice until significant thinning occurs. On the other hand, hair may also fall out quickly, leading to sudden and noticeable changes.

Unlike the general thinning seen in most women, some individuals experience balding around the temples, contributing to the development of an M-shaped hairline.
The Common Causes of Receding Hairlines in Women
Several factors contribute to a receding hairline in women, including:
Genetics
Genetics
Many forms of hair loss are hereditary. If a close family member, such as a mother or grandparent, has a receding hairline, the likelihood of experiencing it increases.
Aging
Aging
Hair tends to fall out more as individuals grow older. Moreover, androgenetic alopecia (female pattern baldness) becomes more common with age. While some women experience it as early as their twenties, nearly half of women in their seventies show signs of female pattern baldness.
Stress
Stress
High-stress levels can sometimes trigger hair loss. This condition, known as telogen effluvium, leads to temporary but noticeable hair thinning. Consequently, managing stress effectively can help mitigate its impact on hair health.
Menopause
Menopause
Hormonal changes during menopause frequently cause hair thinning and, in some cases, significant hair loss. Because of this, addressing hormonal imbalances is essential.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients can contribute to hair loss. Specifically, deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, and biotin are among the most common culprits.
Rapid Weight Loss
Rapid Weight Loss
Losing weight too quickly may also result in telogen effluvium. In fact, many women first notice this type of hair loss around the hairline.
Tight Hairstyles
Tight Hairstyles
Certain hairstyles, such as braids, cornrows, and dreadlocks, place excessive tension on the hair follicles, potentially causing traction alopecia. If the tension persists for extended periods, the damage may become permanent.
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is a specific type of hair loss affecting the front of the scalp. Additionally, it can lead to hair thinning on the eyebrows and eyelashes.
If you are experiencing a receding hairline and are unsure of the cause, seeking medical advice is highly recommended. Various factors, including illness, hormonal fluctuations, or nutritional deficiencies, can contribute to this type of hair loss. While simple lifestyle adjustments or dietary supplements may help restore hair health, genetic factors may require advanced hair restoration treatments.
How to Restore Frontal Hair
Several treatments can help restore your hairline:
1. Hair Loss Medications
Certain medications effectively promote hair regrowth. Among them, minoxidil is the only topical treatment fully approved for women. This over-the-counter solution enhances blood circulation in the scalp and extends the hair growth phase, ultimately improving hair density. To maintain long-term results, daily application is essential.
2. Addressing Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients can contribute to hair thinning. Therefore, undergoing a blood test helps identify deficiencies such as iron deficiency (anemia). When necessary, a doctor may recommend prescription medication or over-the-counter supplements to correct these imbalances.
3. Managing Stress
Since stress plays a significant role in hair loss, adopting stress-reducing habits is beneficial. Engaging in regular exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood and alleviate tension. Furthermore, meditation, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep further support both mental well-being and hair health.
4. Using Hair Oils
Some hair oils encourage hair regrowth. For instance, studies suggest that rosemary oil and pumpkin seed oil can stimulate hair follicles. Interestingly, research indicates that rosemary oil performs comparably to minoxidil in promoting hair growth.
5. Addressing Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly those associated with menopause, often trigger hair loss. Consulting a healthcare professional provides clarity on managing these imbalances. Moreover, maintaining a healthy weight, following a consistent exercise routine, and prioritizing sleep help regulate hormone levels naturally.
6. PRP Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy offers a non-invasive approach to hair restoration. This treatment involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, extracting platelets, and injecting them into the scalp. As a result, healing and blood circulation improve, leading to enhanced hair growth. Many individuals notice visible improvements within six months.
7. Advanced FUE Hair Transplant
In cases where other treatments prove ineffective, a hair transplant may be the most viable option. Women diagnosed with androgenetic alopecia often benefit from follicular unit extraction (FUE), a procedure that transplants individual hair follicles for natural-looking results. This minimally invasive technique results in little to no scarring and promotes a swift recovery. Most patients resume daily activities within a few days. For real-life transformations, explore our testimonial videos showcasing successful hair transplants.
